MRI Treatment Assessment for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Mouse Ankle Model
- 1. Technischen Universität München, Klinikum rechts der Isar / Nuclear Medicine, München, Germany
- 2. Technischen Universität München, Klinikum rechts der Isar / Radiology, München, Germany
Effective drugs are presently available for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), however early diagnosis and monitoring are essential for their optimal use. The choice of therapeutic strategy is based on clinical symptoms, medical imaging, and laboratory parameters, which may be difficult or impossible to use with early-stage disease.
In this study, we seek to assess the utility of MRI for early diagnosis and for treatment monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis using an induced arthritis mouse model.
Collagen-induced arthritis is elicited in DBA/1 mice by immunization with collagen II emulsified in complete Freund's adjuvant. This produces a pathology that shares features with RA, including synovial hyperplasia, an increased synovial gap, and cartilage degradation. Symptoms appear between days 18 and 25, and reach maximum around day 40 after immunization.
The drugs Methotrexat and Prednisolon (M and P) inhibit RA-related inflammatory processes and joint destruction, which may be measured non-invasively with MRI. The novel contrast agent Gadolinium-P in particular is expected to accumulate at higher concentration in RA-related inflamed tissues due to binding with proteins expressed in those areas. The traditional contrast agent Gd-DTPA does not specifically target inflammation.
The study involves three groups of six mice each. In two groups, arthritis is induced, while the third are control animals. In one of the induced groups, animals are treated with M and P i.p. injections once per week. Animals' ankles are scanned at approximately day 1, 32, and 42 after arthritis induction. Clinical scoring is conducted 3 times per week. Postmortem histological analysis will be done on day 42 post-induction.
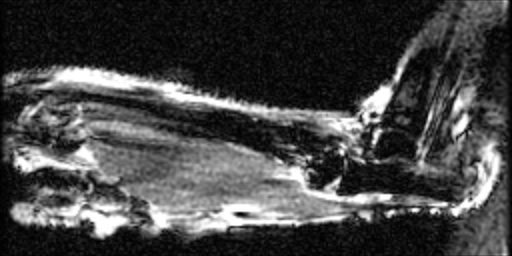
MR images were acquired on a GE/Agilient MR901 7T small animal system, with 2 cm receive coil placed directly on the ankle. A 2D multislice RF-spoiled GRE sequence was used, with a 192x96 matrix, 0.25 mm slice thickness, 15 mm x 7.5 mm FOV, TR 50 ms, TE 3.5 ms, FA 30 degrees, 150 averages, requiring 12 min to acquire. Images were acquired at baseline, and approximately 30 min post i.v. injection of Gado-P or Gadolinium-DPTA.
In the attached images of normal mice, details of the ankle bones and synovial gaps are visible. The tibia and fibula, calcaneum, metatarsals, intermedium, and various tarsals can be distinguished.