The application of low field NMR technology in hydrate formation and dissociation
- Niumag Corporation, Suzhou, China
Gas hydrate is composed of water and low molecular weight gases such as CH4, C2H6, CO2 etc (mainly methane). In recent 20 years, a large amount of gas hydrate are found rich in marine and permafrost, which have got a lot of attention as a kind of potential energy in the whole word. So the study of the mechanism of gas hydrate formation and dissociation is necessary.
Magnetic resonance relaxation analysis is an efficient, non-destructive detection technology, which has been applied in engineering field in recent years. It is a new experiment in the research of gas hydrate.
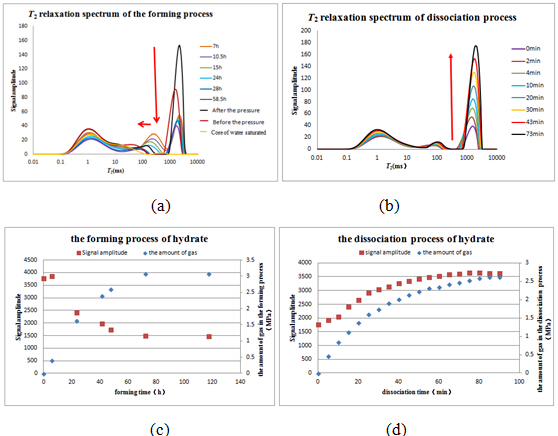
In the experiment of gas hydrate formation and dissociation, the main parameter detection is the relaxation time and the amplitude of the signal.
The relaxation time and the amplitude of the signal can be used to observe the formation of hydrates and quantitative calculation.Because the properties of hydrate and ice are same, so we can set an appropriate TE, the signal of hydrate is decayed, but the signal of water is still exist. We can calculate the amount of hydrate formation by the reduction of the total signal.